LAKE SKADAR
A view from lakeside hill
Photo: CAR & DRIVER
A. LOCATION
- Yugoslavia; and Albania.
- 42:10N, 19:20E; 5 m above sea level.
B. DESCRIPTION
-
Lake Skadar is the largest lake in the Balkan district, situated at the southern end of the Dinaric Alps on the border of Yugoslavia and Albania. It lies about 100 km to the southeast of the famous scenic town of Dubrovnik on the coast of the Adriatic Sea. To the southwest of the lake rise high mountains, while to the northeast stretches a wide swamp. There are many islands in the western part of the lake and a number of spots where ground water spouts up from the bottom (Okos). The lake is considered to have been formed by dissolution of limestone in a tectonic basin during the Tertiary or Quarternary period. It is a shallow lake with 8 m maximum depth and 5 m mean depth.
The Moraca River, which is the largest inflowing stream with cold water heavily loaded with suspended solids, has a great influence upon the transparency and water quality of this lake. The Bojana River flows out from the south end and drains into the Adriatic Sea. The phosphate concentration in the lake water is low, and the low transparency is attributed to the large amount of suspended solids in the inflowing water. The lake is rich in fish and waterfowl fauna.
C. PHYSICAL DIMENSIONS (1)
| Surface area [km2] | 372 |
| Volume [km3] | 1.93 |
| Maximum depth [m] | 8.3 |
| Mean depth [m] | 5 |
| Water level | Regulated |
| Normal range of annual water level fluctuation [m] | 2 |
| Length of shoreline [km] | 207 |
| Catchment area [km2] | 5,490 |
D. PHYSIOGRAPHIC FEATURES
D1 GEOGRAPHICAL- Bathymetric map: Fig. EUR-09-01.
- Number of outflowing rivers and channels (name): 1 (Bojana R.).
- Climatic data at Skadar (3)
| Mean temp. [deg C]*1 | |||||||||||||
| Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Ann. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3.9 | 5.8 | 9.2 | 13.1 | 18.1 | 21.7 | 25.0 | 24.7 | 20.8 | 16.1 | 10.6 | 6.7 | 14.7 | |
| Precipitation [mm]*2 | |||||||||||||
| 137 | 140 | 157 | 132 | 89 | 48 | 46 | 28 | 99 | 198 | 208 | 154 | 1,436 | |
| *1 13-year mean. *2 50-year mean. | |||||||||||||
- Number of hours of bright sunshine: 2,533 hr yr-1.
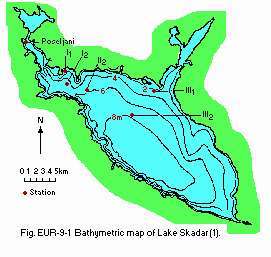
Bathymetric map (1).
- Water temperature: Fig. EUR-09-02.
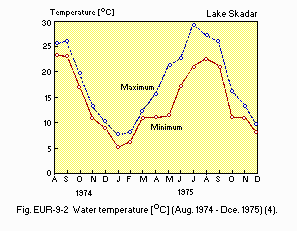
Water temperature [deg C](August 1974-December 1975)(4).
- Freezing period: Only twice in recent years (February 1954 and 1956).
- Notes on water mixing and thermocline formation
The thermocline is not formed.
E. LAKE WATER QUALITY
E1 TRANSPARENCY [m](5)-
Radus, 1977: 4.
| Station I1, 1972-1973 | ||||||||||||
| Depth [m] | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7.2 | - | 7.2 | 8.2 | 7.9 | - | - | 8.0 | 8.0 | 8.2 | 8.0 | - | |
| Station I2, 1972-1973 | ||||||||||||
| 7.8 | - | 8.1 | 8.1 | 8.1 | - | - | 8.2 | 8.2 | 8.1 | 8.0 | - | |
| Station II2, 1972-1973 | ||||||||||||
| 7.8 | - | 7.8 | 7.5 | - | - | - | 8.0 | 8.2 | 8.5 | 8.2 | - | |
| Station III1, 1972-1973 | ||||||||||||
| 7.8 | - | 8.2 | 8.1 | 8.1 | - | - | 8.2 | - | - | - | - | |
| Station III2, 1972-1973 | ||||||||||||
| 8.1 | - | 8.1 | 8.2 | 8.2 | - | - | - | 8.0 | 8.3 | - | - | |
| Poseljani, 1972-1973 | ||||||||||||
| 8.2 | - | 8.2 | - | - | - | - | 8.0 | 8.0 | 8.1 | - | - | |
- NH4-N [mg l-1]
| Station I1, 1972-1973 | ||||||||||||
| Depth [m] | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| .000 | .000 | - | .004 | .080 | .002 | .020 | .020 | .030 | .030 | .010 | .240 | |
| Station I2, 1972-1973 | ||||||||||||
| .010 | .000 | - | .000 | .030 | .000 | .016 | .030 | .020 | .000 | .020 | .030 | |
| Station II2, 1972-1973 | ||||||||||||
| - | .020 | - | .000 | .000 | .003 | .020 | .020 | .000 | .020 | .020 | .020 | |
| Station III2, 1972-1973 | ||||||||||||
| .000 | .000 | - | .000 | .000 | .000 | .050 | .050 | .020 | .050 | .010 | .010 | |
| Poseljani, 1972-1973 | ||||||||||||
| .004 | .004 | - | - | - | .000 | .020 | .020 | .030 | .030 | .080 | .080 | |
- NO3-N [mg l-1]*
| Station I1, 1972-1973 | ||||||||||||
| Depth [m] | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| .113 | .068 | .034 | .041 | .057 | - | .045 | .003 | .079 | .057 | .158 | .102 | |
| Station I2, 1972-1973 | ||||||||||||
| .102 | - | - | .170 | .188 | - | .034 | .004 | .068 | .045 | .136 | .079 | |
| Station II2, 1972-1973 | ||||||||||||
| .041 | - | - | .170 | - | - | .027 | .005 | .181 | .079 | .136 | .072 | |
| Station III2, 1972-1973 | ||||||||||||
| - | .057 | .090 | - | .045 | - | .027 | .003 | .192 | .045 | .102 | - | |
| Poseljani, 1972-1973 | ||||||||||||
| .045 | .045 | .045 | - | .000 | - | .027 | .003 | - | .045 | - | .057 | |
| * Converted from the original determination of NO3. | ||||||||||||
- PO4-P [mg l-1]
| Station I1, 1972-1973 | ||||||||||||
| Depth [m] | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| .008 | .002 | - | .001 | .002 | - | .003 | .002 | .006 | .002 | .003 | .007 | |
| Station I2, 1972-1973 | ||||||||||||
| .002 | .000 | - | .002 | .002 | - | .003 | .017 | .007 | .000 | .002 | .007 | |
| Station II2, 1972-1973 | ||||||||||||
| .002 | - | - | .000 | .014 | - | .003 | .005 | .003 | .010 | .010 | .007 | |
| Station III2, 1972-1973 | ||||||||||||
| .002 | .003 | - | .002 | .002 | - | - | - | - | .003 | .002 | .007 | |
| Poseljani, 1972-1973 | ||||||||||||
| .003 | .002 | - | - | .012 | - | - | .004 | .004 | .002 | .040 | .003 | |
F. BIOLOGICAL FEATURES
F1 FLORA- Emerged macrophytes (7)
Scirpus lacustris, Phragmites communis, Typha angustifolia. - Floating macrophytes: Nymphaea alba, Nuphar luteum, Trapa natans (7).
- Submerged macrophytes: Myriophyllum, Ceratophyllum, Potamogeton spp. (7).
- Phytoplankton (8)
Cyclotella glomerata, C. Planctonia, Pediastrum, Ceratium hirundinella, Microcystis, Merismopedia, Dinobryon divergens, D. bavaricum.
- Zooplankton: Rotatoria, Cladocera, Copepoda, Protozoa (9).
- Benthos: Chironomidae, Oligochaeta, Bivalvia, Gastropoda (10).
- Fish (11): Alburnus, Cyprinus, Chondrostoma, Anguilla, Salmo, Rutilus, Alosa, Pachychilon, Mugil, Scardinius.
N. SOURCES OF DATA
- Beeton, A. M. (1981) General introduction. The Biota and Limnology of Lake Skadar (ed. Karaman, G. S. & Beeton, A. M.), pp. 15-17. University of "Veljko Vlahovic", Smithsonian Institution of Washington, and Centre for Great Lakes Studies/University of Wisconsin, Titograd.
- Lasca, N. P., Radulovic, V., Ristic, R. J. & Cherkauer, D. S. (1981) Geology, hydrology, climate and bathymetry of Lake Skadar. Ibid., pp. 17-38.
- Air Ministry Meteorological Office (1958) Tables of Temperature, Relative Humidity and Precipitation for the World. Part III. Her Majesty's Stationery Office, London.
- Beeton, A. M. (1981) Water masses, thermal conditions and transparency of Lake Skadar. The Biota and Limnology of Lake Skadar (see above), pp. 38- 55.
- Torke, B. (1981) Growth rates of crustacean zooplankton in Lake Skadar. Ibid., pp. 217-219.
- Petrovic, G. (1981) Chemical investigations of water and sediments of Lake Skadar. Ibid., pp. 68-96.
- Ristic, J. & Vizi, O. (1981) Synoptic survey of the dominant macrophytes in Lake Skadar. Ibid., pp. 117-125.
- Petkovic, S.(1981) Phytoplankton. Ibid., pp. 163-189.
- Petkovic, S.(1981) Zooplankton. Ibid., pp. 191-199.
- Karaman, G. S. & Nedic, D. (1981) Zoobenthos of Lake Skadar. Ibid., pp. 222-246.
- Stein, R. A., Mecom, J. O. & Ivanovic, B. (1981) Commercial exploitation of fish stocks in Lake Skadar, 1947-1976. Ibid., pp. 343-354.

