LAKE BALATON
From the rooftop of Balaton Limnological Research
Institue, Tihany

Photo: A. Kurata
A. LOCATION
- Somogy and Veszprem, Hungary.
- 46:42-47:04N, 17:15-18:10E; 104.8* m above sea level.
* Adriatic.
B. DESCRIPTION
Lake Balaton was formed mainly by tectonic
forces 12,000-20,000 years ago. Prior to the opening of Sio-canal
in 1863, its water level was 3 m higher and its surface was about
twice larger than at the present. With its surface area of 593
km2, Lake Balaton is the largest lake in Central Europe, but
its mean depth is only 3.2 m.
The main inflow, the Zala River, empties
into the southwestern end of the lake, while the Sio-canal drains
the water from the eastern basin into the River Danube.
The lake is covered by ice in winter. In
summer the average water temperature is 23deg C. The strong waves
swirl up much sediments, rendering the transparency low.
The major ions of the water are Ca2+, Mg2+
and HCO3-. The pH is 8.4, rising to higher values during intensive
primary production. Oxygen deficiency is formed only temporarily
in the western part of the lake in calm summer periods with algal
blooms.
The distribution of macrophytes is restricted
by strong waves to a relatively narrow belt. Only 3 percent of
the lake surface is covered by reeds, and even less by submerged
macrophytes. The major primary producers are phytoplankton. Zooplankton
is not abundant. Zoobenthos represents an important food for
the fish. The annual commercial fish catch is 1200 tons.
The southern shore of the lake consists
of sandy beach, while on the northern shore there are mountains
of volcanic origin with old ruins on their tops and vineyards
on their slopes. The picturesque landscape and the water ideal
for swimming and other water sports attract 2 million tourists
annually.
The sewage discharge from rapidly developing
towns in the watershed, the growing use of fertilizers in agriculture
and large animal farms increased the nutrient loading to the
lake in the last decades. A rapid eutrophication became apparent
by increased production and biomass of phytoplankton. Blooms
of blue-green algae are frequent in the most polluted western
part of the lake.
A eutrophication
control program has been formulated, based on intensive scientific
researches. Most of the municipal sewage is now diverted from
recreational areas. Phosphorus removal was introduced at other
sewage treatment plants. A reservoir was constructed to retain
the nutrients carried by the Zala River. Pollution due to liquid
manure was reduced. Construction of more reservoirs on major
tributaries of the lake and a soil protection program are in
progress (Q).
C. PHYSICAL DIMENSIONS
| Surface area [km2] | 593 |
| Volume [km3] | 1.9 |
| Maximum depth [m] | 12.2 |
| Mean depth [m] | 3.3 |
| Water level | Regulated |
| Normal range of annual water level fluctuation [m] | 0.3 |
| Length of shoreline [km] | 236 |
| Residence time [yr] | 2 |
| Catchment area [km2] | 5,181 |
D. PHYSIOGRAPHIC FEATURES (2)
D1 GEOGRAPHICAL
- Bathymetric map: Fig. EUR-04-01.
- Names of main islands: None.
- Number of outflowing rivers and channels (name): 1 (Sio-canal).
D2 CLIMATIC
- Climatic data at Siofok
| Mean temp. [deg C]*1 | ||||||||||||
| Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Ann. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| -1.4 | 0.6 | 5.0 | 10.7 | 15.6 | 19.4 | 20.8 | 20.2 | 16.3 | 10.8 | 5.6 | 1.0 | 10.4 |
| Precipitation [mm]*2 | ||||||||||||
| 36.5 | 37.7 | 35.6 | 44.7 | 60.4 | 80.8 | 73.3 | 62.4 | 48.4 | 42.9 | 65.5 | 45.7 | 633.9 |
| *1 1947-1963. *2 1951-1980. | ||||||||||||
- Number of hours of bright sunshine (1951-1980): 2,052 hr yr-1.
- Solar radiation (1931-1960): 12.2 MJ m-2 day-1.
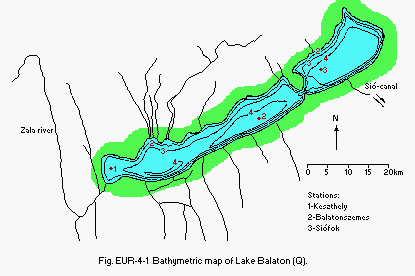
Fig. EUR-04-01
Bathymetric map (Q).
- Water temperature [deg C]
| 1947-1963 | ||||||||||||
| Depth [m] | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | - | - | 4.5 | 11.5 | 17.6 | 21.9 | 23.2 | 22.9 | 19.2 | 13.3 | 6.9 | 2.0 |
- Freezing period (1927-1963): 4 January-24 February.
- Mixing type: Polymictic.
E. LAKE WATER QUALITY (3)
E1 TRANSPARENCY [m]
| Keszthely, 1979-1983 | ||||||||||||
| Depth [m] | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| - | - | 0.49 | 0.38 | 0.50 | 0.47 | 0.50 | 0.35 | 0.41 | 0.46 | 0.50 | 0.65 | |
| Szemes, 1979-1983 | ||||||||||||
| - | - | 0.72 | 0.48 | 0.49 | 0.56 | 0.69 | 0.45 | 0.64 | 0.53 | 0.60 | 0.52 | |
| Siofok, 1979-1983 | ||||||||||||
| - | - | 0.71 | 0.45 | 0.45 | 0.71 | 0.67 | 0.55 | 0.69 | 0.70 | 0.57 | 1.25 | |
E2 pH
8.4, rising to 8.9 in the western part of the lake during summer algal blooms.
E3 SS [mg l-1]
| Keszthely, 1979-1983 | ||||||||||||
| Depth [m] | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | - | - | 34.1 | 39.6 | 27.6 | 40.6 | 23.1 | 31.7 | 23.4 | 25.8 | - | 14.5 |
| Szemes, 1979-1983 | ||||||||||||
| 1 | - | - | 20.7 | 22.2 | 22.5 | 13.9 | 16.4 | 29.1 | 13.5 | 22.6 | 56.0 | 13.4 |
| Siofok, 1979-1983 | ||||||||||||
| 1 | - | - | 16.1 | 19.7 | 23.9 | 13.7 | 25.0 | 23.1 | 13.6 | 18.6 | 20.1 | 4.9 |
E4 DO [mg l-1]
The dissolved O2 concentration is usually close to the saturation level. Strong oversaturation at the surface and O2 deficiency near bottom sediment are found only in the western part of the lake in calm summer periods during algal blooms.
E5 COD [mg l-1]
- Determined by KMnO4 method.
| Keszthely, 1979-1983 | ||||||||||||
| Depth [m] | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | - | - | 7.86 | 8.60 | 6.50 | 7.38 | 9.80 | 7.72 | 7.96 | 8.00 | 8.07 | 9.80 |
| Szemes, 1979-1983 | ||||||||||||
| 1 | - | - | 5.96 | 5.10 | 5.00 | 4.68 | 6.32 | 5.64 | 6.04 | 6.45 | 5.95 | 5.00 |
| Siofok, 1979-1983 | ||||||||||||
| 1 | - | - | 4.88 | 4.80 | 4.02 | 3.26 | 4.70 | 4.46 | 4.46 | 4.67 | 4.43 | 4.90 |
E6 CHLOROPHYLL CONCENTRATION [micro g l-1]
| Keszthely, 1979-1983 | ||||||||||||
| Depth [m] | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | - | - | 34.0 | 30.8 | 19.8 | 20.4 | 33.5 | 51.4 | 38.4 | 41.4 | 42.8 | 42.9 |
| Szemes, 1979-1983 | ||||||||||||
| 1 | - | - | 12.4 | 19.4 | 10.6 | 7.4 | 8.8 | 22.6 | 19.5 | 16.7 | 15.4 | 16.1 |
| Siofok, 1979-1983 | ||||||||||||
| 1 | - | - | 7.2 | 9.2 | 8.5 | 4.4 | 5.4 | 9.8 | 11.7 | 10.0 | 6.8 | 5.1 |
E7 NITROGEN CONCENTRATION
- Total-N [mg l-1]
| Keszthely, 1979-1983 | ||||||||||||
| Depth [m] | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | - | - | 1.81 | 1.85 | 1.23 | 1.50 | 1.39 | 2.01 | 1.51 | 1.57 | 1.72 | 1.94 |
| Szemes, 1979-1983 | ||||||||||||
| 1 | - | - | 1.25 | 0.98 | 0.90 | 0.92 | 0.87 | 0.99 | 0.87 | 1.19 | 1.09 | 0.63 |
| Siofok, 1979-1983 | ||||||||||||
| 1 | - | - | 0.93 | 0.80 | 0.72 | 0.61 | 0.70 | 0.79 | 0.71 | 1.07 | 0.69 | 0.59 |
E8 PHOSPHORUS CONCENTRATION
- Total-P [mg l-1]
| Keszthely, 1979-1983 | ||||||||||||
| Depth [m] | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | - | - | .075 | .089 | .068 | .089 | .101 | .104 | .114 | .089 | .143 | .078 |
| Szemes, 1979-1983 | ||||||||||||
| 1 | - | - | .032 | .052 | .036 | .033 | .035 | .037 | .039 | .040 | .059 | .043 |
| Siofok, 1979-1983 | ||||||||||||
| 1 | - | - | .024 | .028 | .034 | .022 | .027 | .028 | .033 | .043 | .031 | .028 |
F. BIOLOGICAL FEATURES
F1 FLORA (4)
- Emerged macrophytes: Phragmites australis, Typha latifolia.
- Floating macrophytes
Lemna minor, L. trisulca, L. gibba, Spirodela polyrrhiza, Wolffia arrhiza, Hydrocharis morsus-ranae, Nymphaea alba, Nuphar luteum, Trapa natans. - Submerged macrophytes
Potamogeton perfoliatus, P. crispus, P. pectinatus, Najas marina, Stratiotes alloides, Ceratophyllum demersum, Myriophyllum spicatum. - Phytoplankton
Spring Nitzschia acicularis, Cyclotella ocellata, C. bodanica, Stefanodiscus hantzschii. Summer: Eastern part Ceratium hirundinella, Melosira granulata, Botryococcus braunii. Summer: western part Anabaenopsis raciborskii, Anabaena spiroides, A. aphanizomenoides, Aphanizomenon flos-aquae.
F2 FAUNA (5)
- Zooplankton
Polyarthra vulgaris, Keratella quadrata, Pompholyx sulcata. Daphnia cucullata, D. galeata, Eudiaptomus gracilis, Mesocyclops leucarti, Cyclops vicinus. - Benthos
Ectinosoma abrau, Darwinula stevensoni, Potamothrix hammoniensis, Tanypus punctipennis, Lithoglyphus naticoides, Dreissena polymorpha. - Fish
Abramis brama*, Cyprinus carpio*, Stizostedion lucioperca*, Aspius aspius, Pelecus cultratus, Esox lucius, Anguilla anguilla*. * Economically important.
F3 PRIMARY PRODUCTION RATE [mg C m-2 day-1](6, 7)
| Keszthely, 1973 | ||||||||||||
| Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Ann. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 312 | 447 | 524 | 594 | 726 | 858 | 6,640 | 6,628 | 2,265 | 126 | 434 | 373 | 613* |
| Szemes, 1976 | ||||||||||||
| 127 | 96 | 447 | 432 | 496 | 988 | 1,551 | 1,132 | 841 | 386 | 214 | 159 | 210* |
| Siofok, 1977 | ||||||||||||
| 103 | 105 | 248 | 616 | 633 | 951 | 1,228 | 847 | 638 | 313 | 203 | 41 | 181* |
| * [g C m-2 yr-1]. | ||||||||||||
F4 BIOMASS
- Zooplankton: 2.5 [g (dry wt.) m-2].
- Zoobenthos: 2.7 [g (dry wt.) m-2].
- Fish [ton(wet wt.) per lake]
Abramis brama: 9578. Stizostedion lucioperca: 578.
F5 FISHERY PRODUCTS
- Annual fish catch [metric tons]
1985: 1,315.
F6 PAST TRENDS: Fig. EUR-04-02, 03, 04, 05 and 06.
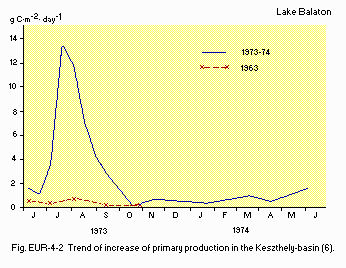
Fig. EUR-04-02
Trend of increase of primary production in the Keszthely-basin
(6).
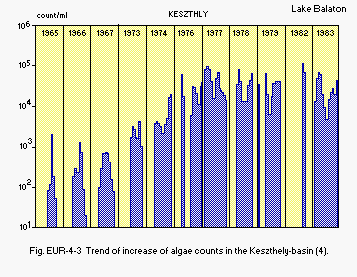
Fig. EUR-04-03
Trend of increase of algae counts in the Keszthely-basin (4).
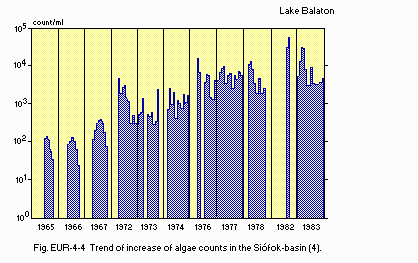
Fig. EUR-04-04
Trend of increase of algae counts in the Siofok-basin (4).
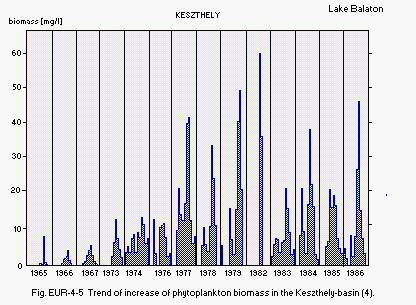
Fig. EUR-04-05
Trend of increase of phytoplankton biomass in the Keszthely-basin
(4).
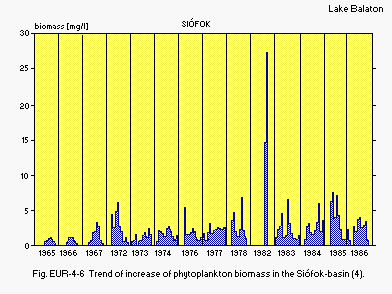
Fig. EUR-04-06
Trend of increase of phytoplankton biomass in the Siofok-basin
(4).
G. SOCIO-ECONOMIC CONDITIONS (8)
G1 LAND USE IN THE CATCHMENT AREA
1982
| Area [km2] | [%] | |
|---|---|---|
| - Natural landscape | ||
| Woody vegetation | 1,343 | 25.9 |
| Herbaceous vegetation | 362 | 7.0 |
| Swamp | 106 | 2.0 |
| - Agricultural land | ||
| Crop field | 2,428 | 46.9 |
| Pasture land | 505 | 9.7 |
| - Residential area | 437 | 8.4 |
| - Others | - | - |
| - Total | 5,181 | 100.0 |
- Main types of woody vegetation
Deciduous forest (Carpinus betulus, Quercus petraea, Acer campestris, Quercus pubescens, Quercus cerris, Fraxinus ornus). - Main kinds of crops: Wheat, maize, hay, grape and fruits.
- Levels of fertilized application on crop fields
Heavy (121 kg N + 90 kg P2O5 + 126 kg K2O ha-1 yr-1).
G2 INDUSTRIES IN THE CATCHMENT AREA AND THE LAKE
| 1980 | |||
| No. of persons engaged | No. of establishments | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Primary industry | 46,400 | ||
| Animal husbandry | 334 | ||
| Secondary industry | 65,200 | 741 | |
| Tertiary industry | 78,900 | ||
- Numbers of domestic animals in the catchment area
Cattle 90,000, Sheep 110,000, Swine 220,000, Poultry 1,500,000.
G3 POPULATION IN THE CATCHMENT AREA
| Population | Population density [km-2] | Major cities (population) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Urban | 180,500 | Zalaegerszeg, Tapolca, | |
| Rural | 224,300 | Marcali, Keszthely, | |
| Total | 404,800 | 64 | Siofok, Balatonfured |
H. LAKE UTILIZATION
H1 LAKE UTILIZATION
Source of water, navigation and transportation, sightseeing and tourism (no.of visitors in 1982: 1,800,000), recreation (swimming, sport-fishing,yachting) and fisheries.
H2 THE LAKE AS WATER RESOURCE
| Use rate [m3 sec-1] | |
|---|---|
| Domestic | 0.273 |
| Irrigation | 0.079 |
| Industrial | 0.330 |
| Power plant | - |
| Others | - |
I. DETERIORATION OF LAKE ENVIRONMENTS AND HAZARDS
I1 ENHANCED SILTATION
- Extent of damage: Not serious.
I2 TOXIC CONTAMINATION (9)
- Present status: Detected but not serious.
- Main contaminants, their concentrations and sources (lake average)
| Name of contaminant | Range of concentration [ppm] in*1 | Main sources | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water | Bottom mud | Fish*2 | Other organisms | ||||
| 1982 | 1984 | 1982 | 1982*3 | 1982*4 | 1982*5 | ||
| Cu | (0.005) | (10) | (3.12) | (12.3) | (18.6) | (42.5) | Waste |
| Zn | (0.057) | (90) | (64.3) | (468) | (73.5) | (111) | dumps and |
| Ca | (0.0008) | (1.5) | (0.65) | (3.7) | (3.99) | (1.47) | agriculture |
| Hg | (0.0007) | (-) | (0.36) | (1.22) | (1.88) | (1.08) | |
| Pb | (0.002) | (30) | (3.59) | (48.5) | (22.1) | (12.3) | |
| *1 For water on volume basis mg l-1; for bottom mud, fish and other organisms on dry weight basis mg kg-1. | |||||||
| *2 Abramis brama, muscle. | |||||||
| *3 Anodonta oygnea, pill. | |||||||
| *4 Chironomidae larvae, whole animals. | |||||||
| *5 Crustacean plankton. | |||||||
I3 EUTROPHICATION
- Nuisance caused by eutrophication
Unusual algal bloom (Dominant species of algae Aphanizomenon flos-aquae, Anabaenopsis raciborskii, Anabaena aphanizomenoides, Anabaena spiroides). - Nitrogen and phosphorus loadings to the lake [t yr-1]
whole lake basin,
| 1975-1981 | ||||||
| Sources | Industrial | Domestic | Agricultural | Natural | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T-N | - | 382 | 1,973 | - | 3,148 | |
| T-P | - | 89 | 150 | - | 314 | |
- Supplementary notes
The following measures are being taken to prevent further eutrophication. - Development of sewerage and sewage treatment plants.
- Phosphorus removal at sewage treatment plants.
- Diversion of a greater part of treated effluents produced in recreational areas from the watershed of the lake.
- Establishment of reservoirs on larger tributaries to retain plant nutrients.
- Elimination of large livestock breeding farms from the watershed or the assurance of full agricultural utilization of their wastes (mainly liquid manure).
- Removal of the surface layer of lake sediments in areas of high phosphorus accumulation.
- Land reclamation and soil amelioration.
J. WASTEWATER TREATMENTS (Q)
J1 GENERATION OF POLLUTANTS IN THE CATCHMENT AREA
f) Extensive development of the catchment area with provision for municipal wastewater treatment.
J3 SANITARY FACILITIES AND SEWERAGE
- Percentage of municipal population in the catchment area
provided with
adequate sanitary facilities (on-site treatment systems) or public sewerage: 100%. - Percentage of rural population with adequate sanitary facilities
(on-site
treatment systems): 100%. - Municipal wastewater treatment systems
No. of tertiary treatment systems: 6 (64,000 m3 day-1); P removal by aluminum sulphate. No. of secondary treatment systems: 17 (75,000 m3 day-1).
M. LEGISLATIVE AND INSTITUTIONAL MEASURES FOR UPGRADING LAKE ENVIRONMENTS
M1 NATIONAL AND LOCAL LAWS CONCERNED
- Names of the laws (the year of legislation)
- Hungarian Water Act (1964)
- Environment Protection Act (1976)
- Revision of the Water Resources Development Program of the Lake Balaton Area (1979)
- Resolution of the Council of Ministers on Restoration of Water Quality of Lake Balaton (1983)
- Responsible authorities
- National Water Authority
- Ministry of Public Health
- Ministry of Agriculture
- Ministry of Construction and Town Development
- National Authority for Environment Protection and Nature Conservation
M2 INSTITUTIONAL MEASURES
- National Water Authority
M3 RESEARCH INSTITUTES ENGAGED IN THE LAKE ENVIRONMENT STUDIES
- Balaton Limnological Research Institute of the Hungarian Academy of Sciences, Tihany
- Research Centre for Water Resources Development
- National Public Health Institute
- Karl Marx University of Economics
- Scientific and Design Institute for Urban Planning
- Institute for Environmental Protection
- Supplementary notes
Thirty other research institutes, university chairs and other agencies participated in the research program coordinated by the above institutions.
N. SOURCES OF DATA
- Questionnaire filled by Dr. S. Herodek, Balaton Limnological Research Institute of the Hungarian Academy of Sciences, Tihany.
- Illes I. (ed.)(1981) Our Lake Balaton. Natura Press, Budapest (in Hungarian).
- National Meteorological Service-Data Bank.
- Research Centre for Water Resources Development-Data Bank.
- Voros, L. (1985) Phytoplankton changes in space and time in Lake Balaton. D. Sc. Thesis (in Hungarian).
- Ponyi, J. E. (1986) Pelagic and benthic invertebrates of Lake Balaton and their ecology. D. Sc. Thesis (in Hungarian).
- Herodek, S. & Tamas, G. (1976) The primary production of phytoplankton in the Keszthely-basin of Lake Balaton in 1973-1974. Annal. Biol. Tihany, 42: 175-190.
- Herodek, S., Voros, L. & Toth, F. (1982) The mass and production of phytoplankton and the eutrophication in Lake Balaton III. The Balatonszemes basin in 1976-1977 and the Siofok basin in 1977. Hidrol. Kozl., 62: 220-229 (in Hungarian with English summary).
- National Authority for Environment Protection and Nature Conservation (1984) Balaton 1982.
- Salanki, J. V., Balogh, K. & Berta, E. (1982) Heavy metals in animals of Lake Balaton. Water Research, 16: 1147-1152.


